Traditional Chinese Medicine in Skincare: Evaluating the Evidence

Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has been a cornerstone of holistic health practices, revered for its comprehensive approach to wellness. Now, its time-tested principles are increasingly being adopted in the realm of skincare. 🧴 But how effective are these ancient methods in a modern context? We’ll dive into the depths of TCM, meticulously examining the scientific evidence behind popular claims and exploring how you can apply these strategies safely and effectively in your skincare regimen.
—
Understanding Traditional Chinese Medicine in Skincare
The Foundation of Chinese Medicine
TCM is rooted in thousands of years of practice and observation, prioritizing balance, harmony, and the flow of Qi (energy) within the body. When it comes to skincare, practitioners focus on detoxification, nourishment, and balancing the body’s internal energy systems to improve the health and appearance of the skin.
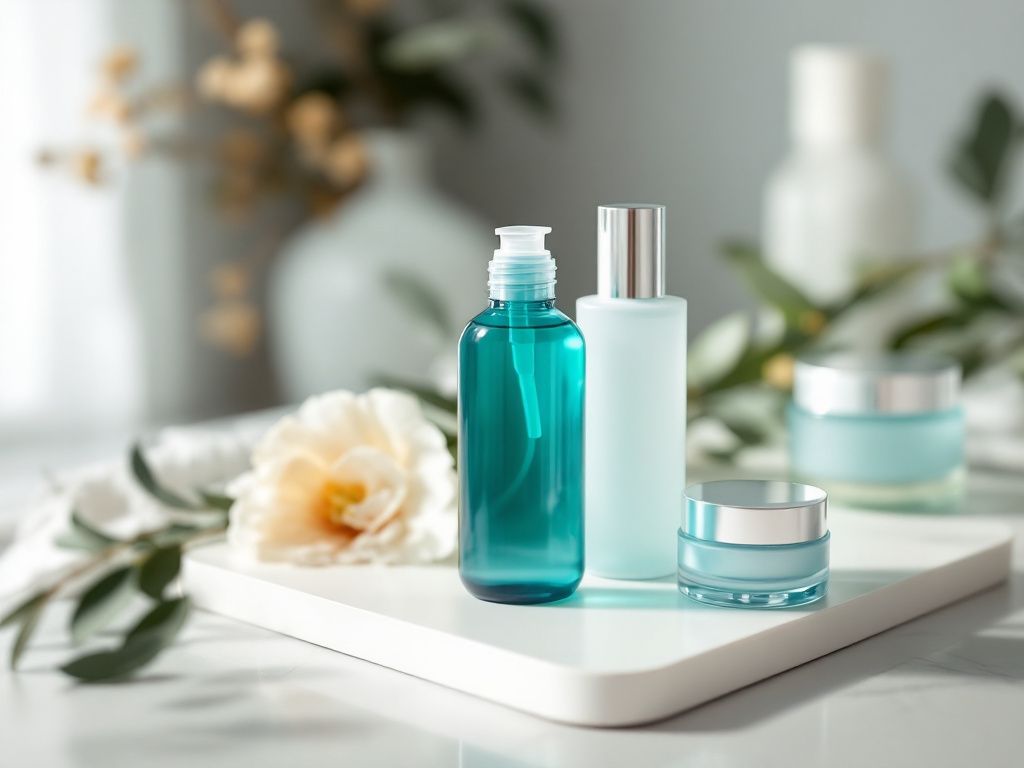
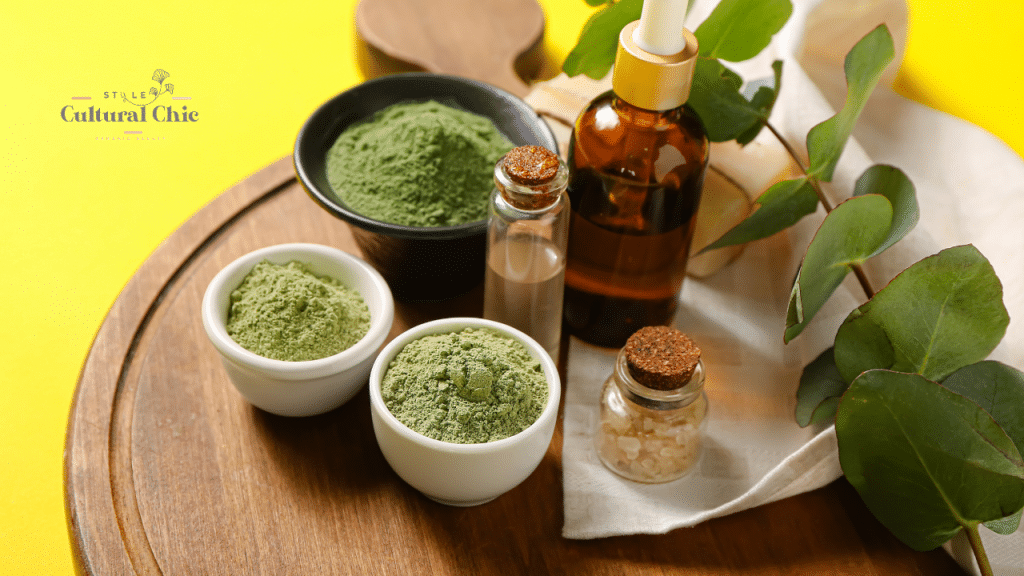
Common TCM Ingredients in Skincare
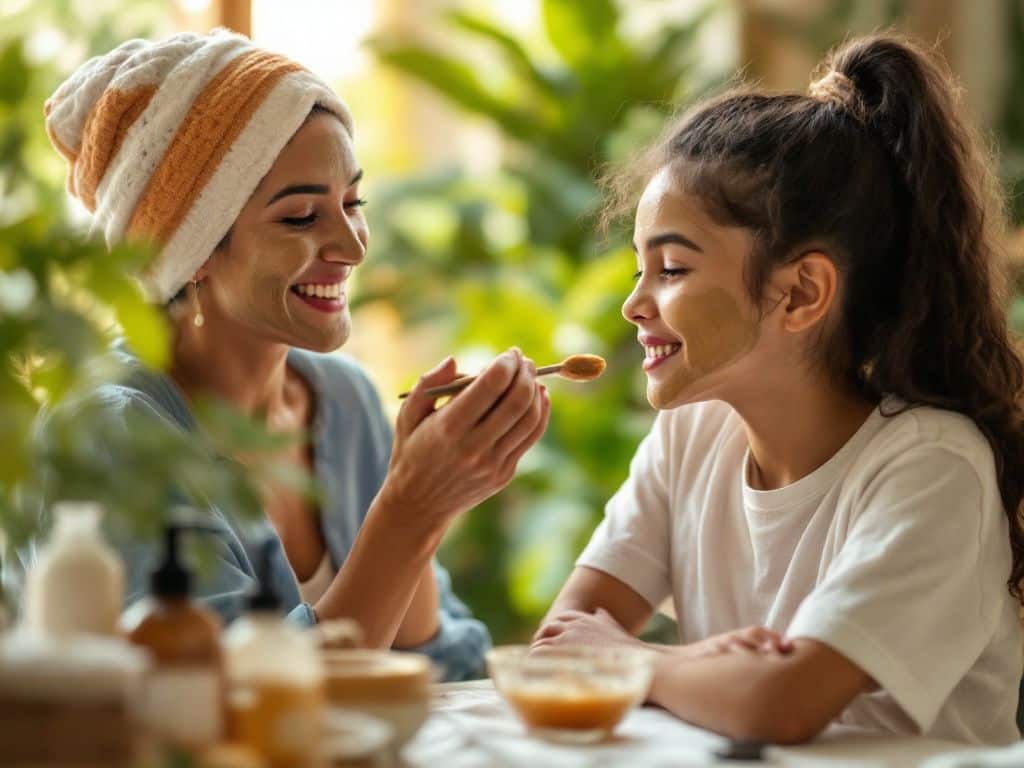
Many TCM ingredients have made their way into modern skincare. These include:
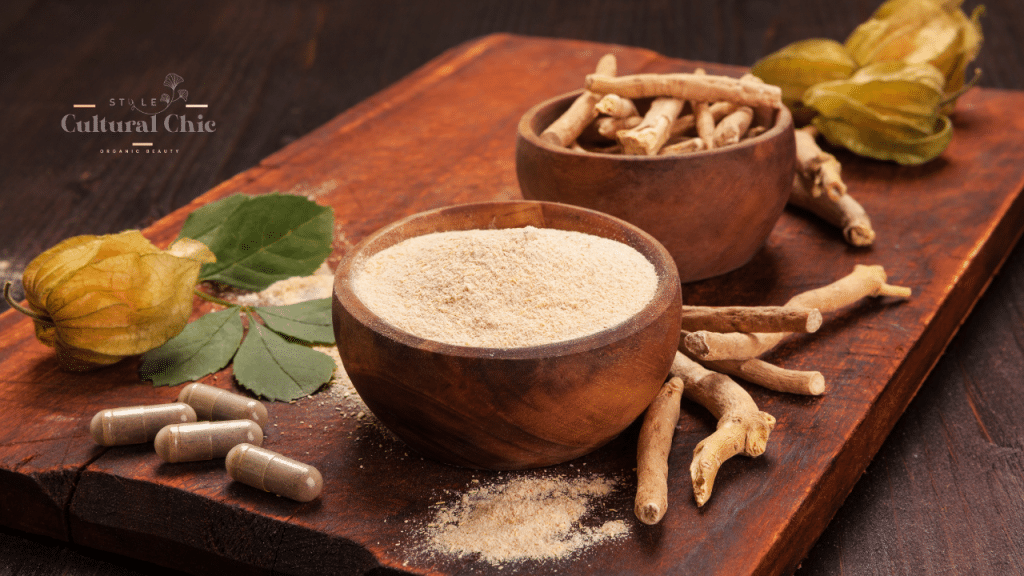
- Ginseng: Known as the “root of immortality,” ginseng is praised for boosting circulation and combatting aging.
- Licorice Root: Used for its anti-inflammatory and brightening properties.
- Green Tea: Rich in antioxidants, it is believed to protect the skin from environmental stressors.
- Goji Berries: High in vitamins and minerals, touted for their firming and anti-aging benefits.
But what does science say about these age-old remedies when they’re applied to the skin? Let’s delve into the evidence. 📚
—
Scientific Validation of Key TCM Ingredients

Ginseng: The Circulation Booster
Scientific studies validate multiple skincare benefits of ginseng. It has been found to improve blood circulation, which can help provide the skin with essential nutrients and oxygen. This is corroborated in a study published in *The Journal of Ginseng Research*, showing its potential to mitigate wrinkles and promote elasticity.
Practical Application:
- Use: Consider a ginseng-infused serum or sheet mask.
- Tip: Apply products in the evening when the skin is in its repair mode for maximum absorption.
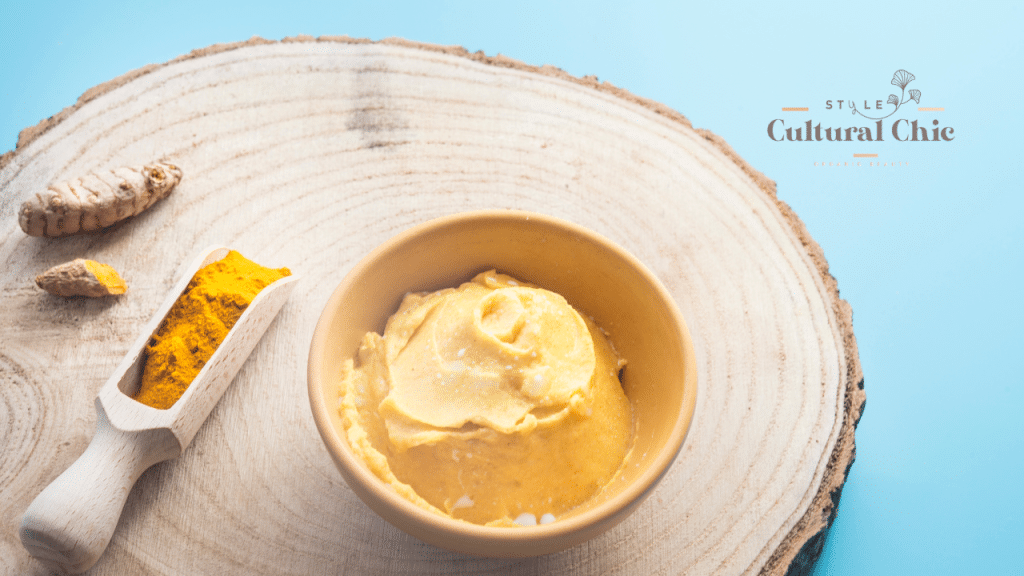
Licorice Root: The Brightening Agent
Research in dermatology journals has highlighted glycyrretinic acid, an active compound in licorice root, known for soothing irritated skin and fading hyperpigmentation. The *Journal of Natural Products* reports its effectiveness in reducing dark spots over time.
Practical Application:
- Use: Choose serums or gels targeting dark spots or uneven skin tone.
- Tip: Patch test first, as its potency may irritate sensitive skin.
Green Tea: The Antioxidant Warrior
The high concentration of polyphenols in green tea is linked to protection against photodamage and improvement in microcirculation. A study in the *International Journal of Cosmetic Science* supports its use in minimizing sun damage and reducing signs of aging.
Practical Application:
- Use: Incorporate green tea-rich moisturizers or cleansers into your routine.
- Tip: Use in morning routines to arm your skin against daily UV exposure.
Goji Berries: The Firming Elixir
Goji berries, abundantly used in TCM, carry a wealth of amino acids, enhancing skin hydration. The *Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics* finds inherent anti-aging effects due to their vitamin content and antioxidant properties.
Practical Application:

- Use: Try incorporating goji berry face creams.
- Tip: Utilized nightly, the increased nutrients support skin renewal during your sleep cycle.
—
Dosage and Product Formulations: Getting it Right
It’s one thing to know the ingredients, but proper usage is paramount. Dosage and form matter — too little, and you may see no effect; too much, and you risk irritation.
Do This, Not That:
- Do: Opt for products from reputable brands with third-party testing.
- Not: DIY concoctions with TCM herbs can be problematic if not prepared correctly; avoid unverified online recipes.
Expert Tip:
Many TCM ingredients work best in synergistic formulas rather than as standalone treatments. Consulting with a dermatologist familiar with both Western and Eastern medicine can provide a more tailored approach.
—
Evidence Against Over-Generalizing Efficacy
While TCM holds great potential, not every ingredient is universally effective for everyone. Variability in individual’s skin type, environmental factors, and personal sensitivities can influence outcomes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Going Overboard: More is not always better. Powerful active ingredients in excess can lead to skin barrier damage.
- Ignoring Scientific Evidence: While anecdotal evidence can be fascinating, prioritize peer-reviewed studies when evaluating efficacy.
—

Real-World Application and Consumer Cases
Consider the case of Lily, a consumer seeking natural solutions for her acne-prone skin. She integrated a TCM-inspired regimen focusing on green tea and licorice root. Over six months, changes noted were reduced inflammation and even complexion, aligning with documented benefits in dermatological studies.
Case Study Excerpt:
Lily kept a detailed log of changes in her skin, correlating her results with established research and dosing recommendations. Her progressive improvements highlighted the gradual but affirmatory benefits of scientifically-backed TCM ingredients in skincare.
—
Comprehensive Evidence Summary and Practical Takeaways
Science Meets Tradition
The marriage of TCM principles with scientific research creates a powerful toolkit for achieving balance and health in skincare. Although not a panacea, evidence suggests significant potential when TCM ingredients are used appropriately.
Top Tips for Implementation:
- Patch Test: Always start small, especially with potent actives like ginseng or licorice.
- Consistent Use: Benefits accrue over time, requiring patience and regular application.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Especially for severe skin concerns, a consultation blends personalized advice with holistic care.
Final Verdict:
TCM represents a fascinating and viable adjunct in the world of skincare, offering a comprehensive path rooted in ancient wisdom and reinforced by modern science. Remember, incorporating these remedies thoughtfully and systematically is key to unlocking their full potential. 🌟
—
By delving into both time-honored traditions and robust scientific evidence, you’re equipped to make informed decisions, crafting a skincare regimen that harmonizes with your unique needs. Explore and enjoy the harmonious blend of past and present in your skincare journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of using a hair mask in my hair care routine?
Using a hair mask can provide several benefits, including hydration, smoothing, strengthening, curl definition, heat protection, and damage repair. Hair masks infuse the hair with moisture, help coat the hair shaft to seal split ends, reduce breakage, and protect the hair from heat styling and environmental damage[1][4].
What ingredients should I look for in a hair mask?
Effective hair masks often include ingredients such as coconut oil, argan oil, shea butter, honey, avocado oil, green tea, and coconut water. These ingredients provide nourishment, moisturize, and protect the hair, offering benefits like softening, moisturizing, and protecting against damage[2][5].
How often should I use a hair mask in my routine?
You should use a hair mask whenever your hair feels dry, unmanageable, or in need of intense hydration. This can vary depending on your hair type and needs, but generally, using a hair mask once or twice a week can help maintain healthy and moisturized hair[1][4].
How do I apply a hair mask for the best results?
To apply a hair mask effectively, shampoo your hair first, then apply the mask, focusing especially on the ends where hair tends to be the most damaged. Leave the mask on for anywhere from 10 minutes to overnight, depending on the type of mask and your hair’s needs[1][4].
References












![Scandinavian Skincare Secrets [Revealed]](https://culturalchicstyles.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/10x-Blogs-2-2025-06-18T113546.586-1024x576.png)

![[Beginner's Guide] Must-Have Korean Beauty Products](https://culturalchicstyles.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/10x-Blogs-2-2025-06-16T185259.533-1024x576.png)
















































































![[Ancient Meets Modern] How Hanbang Korean Skincare Is Changing Beauty Trends](https://culturalchicstyles.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/10x-Blogs-83-1024x576.png)

![[Skincare Rituals] Unlock the Ancient Japanese Secret of Double Cleansing](https://culturalchicstyles.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/10x-Blogs-78-1024x576.png)